1. What are differential mode signals and common mode signals
Differential mode signal: AC signal of equal size and opposite direction; when double-ended input, the phase of the two signals differs by 180 degrees.
Common mode signal: equal in size. Same direction. In double-ended input, the two signals are the same.
In a differential amplifier circuit, there are two inputs. When signals of equal size and opposite phase are input at these two terminals, (this refers to the effective signal) the amplifier can produce a large amplification, we call this signal a differential mode signal, and the amplification at this time is called the differential mode amplification.
If a signal of equal size and phase is input at each of the two inputs, (this is actually a signal generated at the upper level due to temperature change (temperature drift), which is a harmful thing), a common mode signal is proposed in order to visualize the temperature drift, and the amplification at this point is called the common mode amplification.
Due to the composition characteristics of the differential amplifier circuit, the common mode signal is not amplified in the differential amplifier circuit, so the common mode amplification is very small (generally less than 1). The calculation formula is also divided into single-ended output and double-ended output, so there are four common mode signals and differential mode signals are the input signal when the differential amplifier is double-ended input.
2. What is differential-mode interference and common-mode interference
The interference on any two power lines or communication lines can be expressed in terms of common mode interference and differential mode interference.)
- Differential mode interference
Differential-mode interference: differential-mode interference is transmitted between two conductors and is symmetrical interference, which is defined as the undesired potential difference between any two current-carrying conductors. The mutual interference generated between the signals, generally using inductive capacitance can be filtered out, is that we often use the 104, or magnetic beads.
Differential mode interference is small in amplitude, low in frequency, and causes less interference.
The current of the differential mode interference is equal in size and opposite in direction (phase). Due to the distributed capacitance of the alignment, inductance, signal alignment impedance discontinuity, and signal return path flow through the unexpected path, etc., the differential mode current will be converted to common mode current.
- Common mode interference
Common mode interference: common mode interference is transmitted between the conductor and ground (chassis) and is asymmetric interference, which is defined as the undesired potential difference between any current-carrying conductor and the reference ground; all output waveforms have this property, and this needs to be filtered using common mode inductors.
In general, common mode interference is large in amplitude and high in frequency, and can also generate radiation through the wire, resulting in greater interference.
Common mode interference generally comes from the power supply.
Common mode interference causes
- the grid string into the common-mode interference voltage.
- radiation interference (such as lightning, equipment arc, nearby radio stations, high-power radiation sources) in the signal line induced common-mode interference, the reason is that the alternating magnetic field produces alternating current, ground – zero circuit area and ground – fire circuit area is not the same, the two circuits are different impedance and other reasons caused by the current size is different.
- The grounding voltage is not the same.
- Common mode interference caused by the internal lines of the equipment to the power line.
Common mode interference current
Common mode interference is generally in the form of common mode interference current, in general, common mode interference current is generated for three reasons:
- the external electromagnetic field in the circuit alignment of all the wires induced voltage (this voltage is equal in magnitude and in phase with respect to the earth), the current generated by this voltage.
- due to the different ground potentials of the devices connected to the two ends of the circuit alignment, the current generated by the drive of this ground potential difference.
- there is a potential difference between the circuit alignment on the device and the earth, so that common mode interference currents are generated on the circuit alignment.
Device if the common mode interference current is generated on its circuit alignment, the circuit alignment will produce strong electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic interference to electronic and electrical product components, affecting the performance index of the product; In addition, when the circuit is not balanced, common mode interference current will be transformed into differential mode interference current, differential mode interference current on the circuit directly produce interference impact. For electronic and electrical products circuit signal line and its circuit: differential mode interference current flowing through the circuit of the wire loop, will cause differential mode interference radiation, this loop is equivalent to a small loop antenna, can radiate magnetic field to space, or receive magnetic field.
How to identify common mode interference
- judged from the source of interference: lightning, the nearby occurrence of electric arc, nearby radio stations or other high-power radiation devices on the cable generated interference for common mode interference.
- judging from the frequency: common mode interference is mainly concentrated in more than 1MHz. This is due to the fact that common mode interference is induced into the cable through space, and this induction is only likely to occur at higher frequencies. There is one exception, when the cable passes next to a very strong source of magnetic field radiation (for example, a switching power supply), it also induces common-mode interference at a lower frequency.
- Measurement with instruments: As long as there is a spectrum analyzer and a current caliper can be measured and judged.
- How to suppress differential-mode-common-mode interference
As the most common and harmful interference in EMC interference, the most direct way to suppress it is filtering, which is an important measure to suppress and prevent common mode interference. The function of the filter is to allow the signal of a particular frequency to pass smoothly, while the signal of other frequencies is subject to greater inhibition, it is essentially a frequency selection circuit, which cuts off the path of electromagnetic interference along the signal line or power line propagation, in addition it is also an effective way to compress the interference spectrum, when the interference spectrum is different from the useful signal band, the filter can be used to filter out the useless interference signal. Therefore, the proper selection and correct use of filters to suppress common mode interference is very important.
If the useful signal is a differential-mode signal and the interfering signal is a common-mode signal, a common-mode inductor can be used to suppress the interfering signal.

Principle of common mode inductor and suppression of interference
When a common-mode current flows through the coil, the common-mode current will increase the inductance of the coil by generating a magnetic field in the same direction due to the co-direction of the common-mode current, making the coil exhibit high impedance and producing a strong damping effect, thus attenuating the common-mode current and achieving the purpose of filtering. When the normal differential mode current in the circuit flows through the common mode inductor, the currents in the same phase winding of the common mode inductor coil to produce the reverse magnetic field and cancel each other, so there is basically no attenuation of normal differential mode current.
If the source of common-mode interference is in the power circuit, Y capacitors can be used to suppress the interference signal.
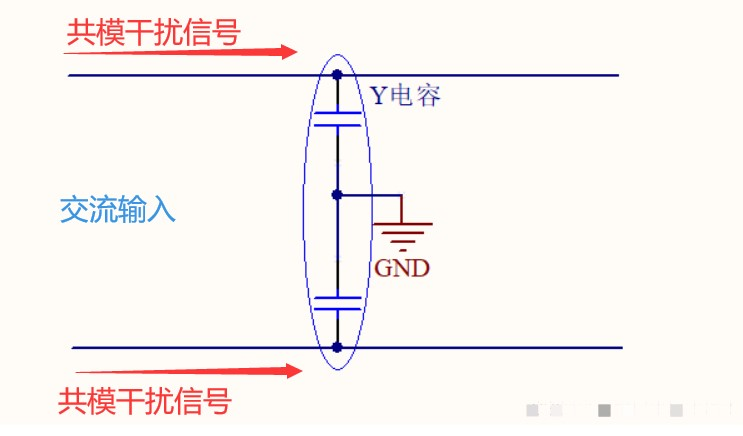
By introducing a Y capacitor into the circuit, the Y capacitor provides the shortest path to bypass the common-mode interference signal, thereby suppressing common-mode interference.
If differential mode interference is also present in the power circuit, X capacitors are used to suppress the interference.
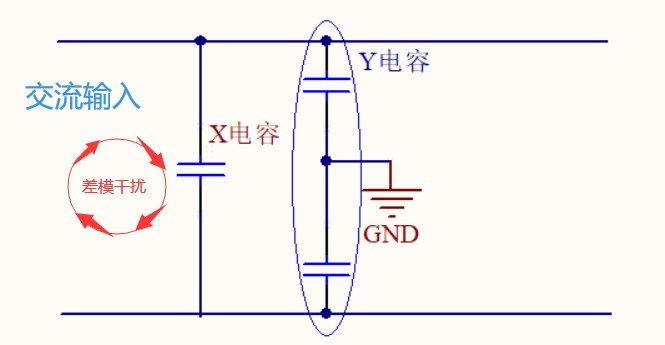
By introducing X-capacitor in the circuit, X-capacitor provides the shortest path to bypass the differential-mode interference signal, thus suppressing the generation of differential-mode interference.
As the most common and harmful EMC interference, common mode interference can be suppressed not only by filtering, but also by shielding the signal line and reducing the ground impedance on the PCB to reduce the common mode signal strength.

