Introduction
With the rapid development of science and technology, automotive electrical functions are becoming more and more complex, from engine control to transmission control, from driving, braking and steering control to safety assurance systems and instrumentation alarm systems, from power management to various efforts to improve comfort, making the automotive electrical system to form a large and complex system, electrical systems through the automotive nerve network – wiring harness system connection The technical requirements for the design, process control, manufacturing and assembly of wiring harnesses are becoming more and more stringent.
Automotive wiring harness terminal crimp voltage drop as an important control indicator of the production of wiring harness, will affect the signal transmission attenuation, distortion, but also affect the service life of the connector, reliability and temperature rise, serious cases will lead to connector ablation melting deformation. Therefore, national standards and major host plants, wiring harness parts factory will be the terminal crimping voltage drop as an important indicator for control. Host plants and harness plants commonly used test methods and determination standards are often not uniform, restricting the development of the harness.
I. The causes of voltage drop in the automotive wiring harness terminal crimp
Terminal crimping is dependent on the mutual contact between the copper wire and the terminal to achieve electrical conduction. From a microphysical point of view, any smooth-looking solid surface is a rough, uneven surface, so the copper wire and the terminal is not a surface contact, is a point contact, the actual contact area is large and small dry visual contact area. As shown in Figure 1.
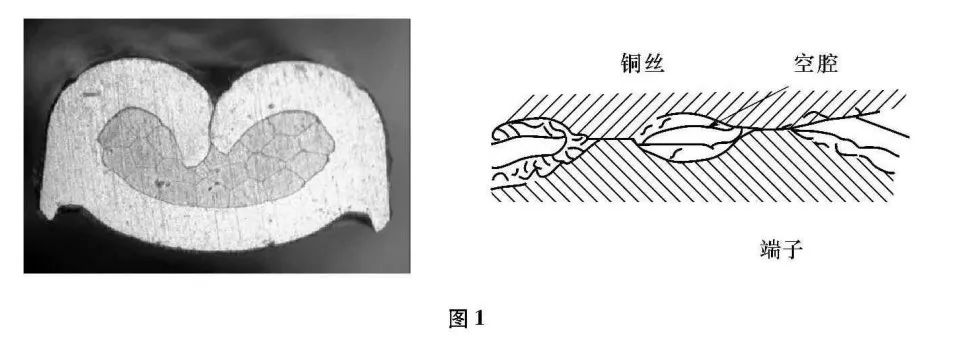
Metal surfaces are generally covered with oxide film and other types of film, in the actual contact range, only part of the film or voltage breakdown to form direct metal-to-metal contact, and most of the film and mutual contact, the current can only actually be called from these “conductive spots” of the contact point through. When the current is conducted through the copper wire and terminal, the current will be concentrated through those very small conductive spots, where the current beam is contracted near the conductive spots, as shown in Figure 2. As the current beam in the conductive spot near the contraction, so that the current flow through the path of growth, the effective conductive area is reduced, so there is a local additional resistance, called the “contraction resistance” or “concentration resistance” expressed in R1.
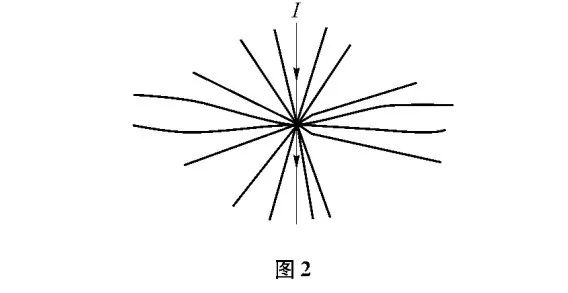
The terminal crimp voltage drop is mainly composed of the following components:R=RI+R2+R3
R1 is the contraction resistance. When the copper wire and the terminal are in contact with each other, their surfaces are not likely to be in complete contact, microscopically, point to point. When the current flows from one contact to another, the current line is subject to contraction and resistance, and thus the resulting resistance is called the contraction resistance.
R2 is the conductor resistance, for the terminal and the sum of the ohmic resistance of the copper wire, its size is determined by the terminal and copper wire selected by the material conductivity, cross-sectional area size and length size, in addition and temperature also have a relationship.
R3 is the film resistance, it is the copper wire and the terminal surface adhesion film, film resistance generated by the
II. Test methods and determination criteria for voltage drop of automotive wiring harness terminal crimp
2.1. “QC/T29106-2004 Automotive low-voltage wire harness technical conditions” terminal crimp voltage drop test method and determination criteria
2.1.1 Terminal voltage drop test method
As shown in Figure 3, measured between the middle of the terminal and the wire crimp to the wire 75mm long wire between the two points, after deducting the voltage drop of the 75mm long wire is the voltage drop of the terminal and the wire crimp. When a terminal is connected to two or more wires at the same time by the current applied to each wire to measure the voltage drop.
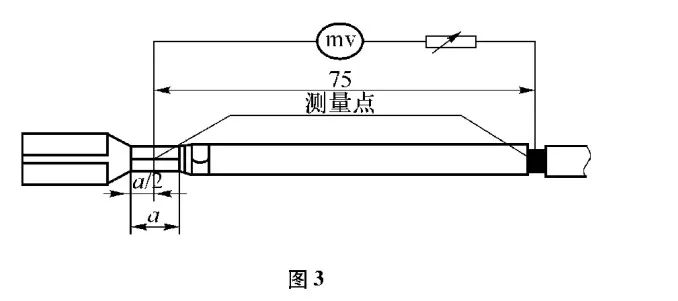
2.1.2 Voltage drop determination criteria
The voltage drop at the connection between the terminal and the wire should be no greater than that specified in Table 1.
Table 1 QC/T29106 voltage drop determination criteria

2.2. “MES67010D wire harness” terminal crimp voltage drop test method and determination criteria
2.2.1 Terminal voltage drop test method
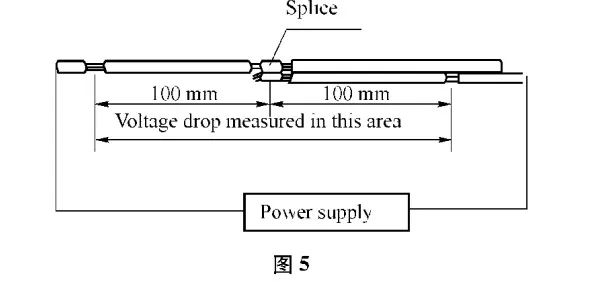
After the wire is energized, the overall voltage drop of the terminal crimp is measured in accordance with Figure 4, or the overall voltage drop of the terminal crimp is measured in accordance with Figure 5, and then the resistance value of the wire is subtracted from the measured value to obtain the voltage drop through the crimped part. Measurement, should be distinguished from the terminal pressure height (C / H) of the minimum value, the middle value and the maximum value. Measurement of the power supply used in its open circuit should be the maximum voltage of 50mV, the maximum current of 100.5mA energized.

2.2.2 Electrical drop determination criteria
The maximum voltage drop of terminal crimp should be 2mV/A, and the maximum voltage drop of terminal should be 3mV/A.
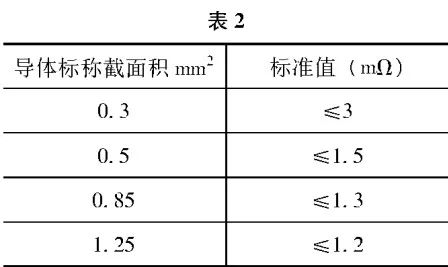
2.3 . 24352NDS00N End Crimp Part Specification” Terminal Crimp Voltage Drop Test Method and Judgment Criteria
2.3.1 Terminal voltage drop test method
(1) When crimping, the conductor compression rate of the copper wire is below 80%, as defined below:

(2) set the end pressure height (C / W) certain, take the same part of the end pressure height (C / W) were the lower value, the middle value, the upper value of the three in accordance with Figure 6 to measure the voltage drop between the crimped part and the wire, minus the resistance of the wire part, you can calculate the contact resistance of the crimped part. Test open-circuit voltage of 20 ± 5mV, short-circuit current of 10 ± 0.5mA.

2.3.2 Voltage drop determination criteria
The voltage drop of the terminal crimp conforms to the provisions of Table 2.
III. Analysis of test conditions for voltage drop in automotive wire harness terminal crimp
3.1 The difference between wires
3.1.1 The difference between wire diameter
Because QC/T29106MES67010 and 24352NDS0O cited wire standards are not the same, the conductor structure (single copper wire diameter and the number of copper wires) is not the same, the nominal diameter of the wire is not the same. Such as QC/T in the wire sample wire diameter including 0.75mm, and no does not include 0.85mm, as shown in Table 4; MES and NDS standards include 0.85 mm, and does not include 0.75mm as shown in Table 5.



3.1.2 The difference between the maximum wire diameter
As shown in Table 6, the maximum size of the wire is not the same because of the QC/T, MES and NDS standards. the maximum nominal diameter in QC/T29106 reaches 70mm2.

3.2 Differences in test conditions
The difference of test conditions, as shown in Table 7
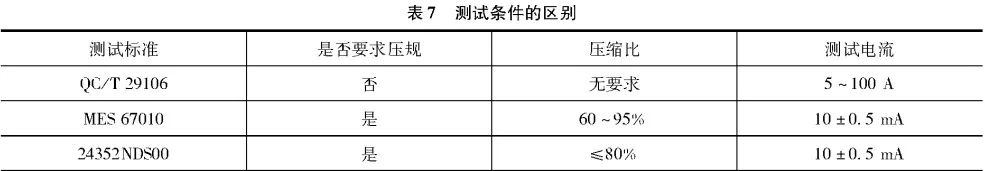
From the crimp gauge (crimp width and crimp height requirements), MES67010 and 24352NDS00 are required to take the maximum value of crimp height, the middle value, and the minimum value of the sample for testing under the condition of a certain crimp width. From the terminal crimping process, it can not guarantee the same pressure gauge of each crimped terminal in mass production, but the value can be between the maximum and minimum crimp height of the test sample, in line with the pressure gauge requirements. Therefore, according to the MES and NDS standards, if the mass-produced parts comply with the pressure gauge, it can be considered that the voltage drop is also qualified. As for QC/T29106, if the test sample terminal crimp height is 12mm, the test voltage drop is qualified, in mass production terminal crimp height is 11mm or 13mm, it is impossible to directly determine whether the voltage drop is qualified. Therefore, the requirements of MES67010 and 24352NDS00 are more reasonable for the test sample pressure gauge.
MES67010 and 24352NDS00 test current is only 10±0.5mA QC/T29106 test current minimum 5A, maximum can reach 100A When using QC/T29106 method testing, when the high current through the test specimen, the test specimen will obviously heat up, while the test specimen will also dissipate heat, need to obtain the real-time temperature of the test specimen, through the temperature correction It is necessary to obtain the real time temperature of the test specimen and calculate the resistance of the test specimen through the temperature correction coefficient, which is more complicated to test and calculate. In contrast, the MES67010 and 24352NDS00 test current is only 10±0.5mA, and the heat generation is very small, so the impact on the calculation of voltage drop is negligible. Therefore, the MES67010 and 24352NDS00 have more reasonable requirements for test current.
IV. Calculation analysis of voltage drop of automotive wire harness terminal crimp
4.1 The difference of wire deduction length
The difference of wire deduction length is shown in Table 8.

MES67010 and 24352NDS00 wire deduction length 100mm, compared to QC/T29106, the whole hundred measurement and calculation is more convenient.
4.2 Calculation of line voltage drop
QC/T 29106 MES 67010 and 24352NDS00 are defined as the voltage drop of the test minus the voltage drop of the wire that is the voltage drop of the terminal crimp. However, for the wire Shen voltage drop is not clearly defined JB/T8139 or IASO D611 voltage drop or measured voltage drop. I believe that the measured voltage drop will be more accurate. JB/T8139 or JASOD611 only clarifies the maximum value of the voltage drop of the wire at 20 ℃, the actual value may be less than the specified value, the actual value is also affected by the temperature, may lead to the terminal crimp voltage drop than the actual value of small.
V. Automotive wiring harness terminal crimp voltage drop determination criteria analysis
QC/T29106 test result determination standard, according to the nominal diameter of the wire from 0.5 ~ 70mm2 changes, the maximum voltage drop for 3 ~ 25mV/A. MES67010 does not distinguish between wire diameter, the maximum voltage drop of the terminal crimp should be 2mV/A, the maximum voltage drop of the terminal should be 3mV/A. 24352NDS00 according to the nominal diameter of the wire from 03 ~ 125mm2 changes, the maximum voltage drop for 1.2 ~ 3mV/A. From the above can be seen that the most lenient determination standard for QC/T29106. The maximum voltage drop is 1.2~3mV/A. It can be seen from the above that the most lenient standard is QC/T29106. 0.5mm2, 0.85mm2 and 1.25mm2 wire diameter, 24352NDS00 is the strictest standard. 0.3mm2 wire diameter, MES67010 is the strictest standard.
VI. Conclusion
This paper introduces the test method and judgment standard of terminal voltage drop in QC/T29106MES67010 and 24352NDS00, and compares them. Through the comparison, it is found that QC/T29106 in the terminal voltage drop test methods and judgment standards and the differences between foreign OEMs, can do more detailed requirements on the terminal crimping and improve the judgment standards.

