Read-only memory has two significant advantages.
1) Simple structure and higher bit density than read/write memory
2) It is non-volatile, so it has high reliability.

ROM is usually used to store system monitoring programs, data tables, etc.
The circuit structure of ROM mainly consists of address decoder, memory matrix and output buffer
The address decoder selects the corresponding memory cell according to the address signal bus. Assuming that the decoder has j address input lines, it can address 2 of j memory cells, then the memory matrix consists of 2 of j memory cells, each of k bits.
The output buffer has a tri-state function and is controlled by the control signal. The data of the memory cell is output to the data bus only when the control signal is valid, otherwise the data bus presents a high resistance state.
As mentioned earlier, ROMs can be divided into five categories with the following characteristics.
1) Mask process ROM (maskrom)
This type of ROM is generally customized by the manufacturer to meet the needs of the user and is suitable for mass production and use. This type of ROM has a simple structure and high integration level, but it is also expensive to produce. This process is only used to customize the required ROM for mass production of a certain stereotyped ROM product.
Memory can be divided into word decoding structure and composite decoding structure in terms of decoding method, and MOS read-only memory is no exception.
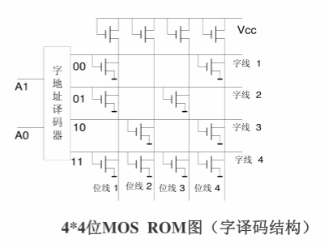
Word decoding structure
The figure below shows a 4*4-bit MOS ROM diagram with a word decoding structure, with two lines of address decoder for two-bit address input, and after decoding, four selection lines are output, each of which selects a word, and the bit line output is the individual bits of the word, i.e., the data line. In the storage matrix shown, some word lines are connected to the MOS tube and some are not, which is determined by the graphics (mask) of the secondary lithograph at the time of manufacture, so it is called mask mode ROM.
For example, when A1A0=01, word line 2 is high, the MOS tube connected to word line 2 is on, bit line 1 and bit line 3 are low and output 0, and the other two bit lines not connected to word line 2 are high and output 1.
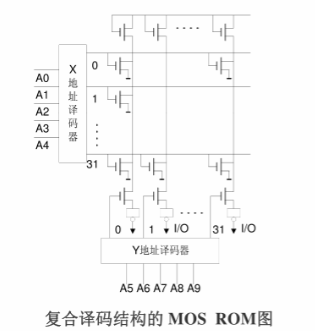
Composite decoding structure
When the number of address lines increases, the number of output lines of the decoder will show an exponential rise and become very large, bringing inconvenience to the process. In the actual design, the composite decoding structure is often used to decode in both directions.
The following figure shows the structure of MOS ROM of 1024*1. 1024 units if the word decoding structure, 10 address lines, there will be 1024 output lines, now the 10 address lines are divided into two groups, respectively, after the line and column decoding, respectively, to produce 32 selection lines, a total of 64, which is much less than 1024.
2) Programmable Read-Only Memory PROM
PROM only allows to write once with programmer, at the factory, the contents of the storage are all 1, and the user can write data 0 to some of the cells as needed to achieve the purpose of programming them.
3) Erasable programmable read-only memory EPROM
This is the most used program memory in China. Its characteristic is that it has erasable function and can be reprogrammed after erasing, so that users can program it again and again, but the disadvantage is that erasure needs to use ultraviolet radiation for a certain period of time.
This type of chip is particularly easy to identify, there is a round window in the center of the chip casing above the “quartz glass window”, in the ultraviolet radiation, the memory of each information changed to 1, that is, erase.
After the erasure, the application program can be cured into the chip by the programmer. With the emergence of a large number of electrically erasable memory devices, EPROM memory is slowly leaving the mainstream market.
4) Electrically erasable programmable read-only memory EEPROM
The biggest advantage is that it can be directly erased and written by electrical signals. It has the non-volatility of ROM and the random read/write characteristics of RAM. However, the content erasure and writing time is long, about 10mS.
It can be read and written by reading and writing operation, and the read and write operation is almost no different from RAM, the difference is that the writing speed is slower, and the information can be saved after power failure. The disadvantage is that the reprogramming time is longer and the number of effective reprogramming is lower, so it cannot replace RAM.
5) Flash Memory ROM (Flash ROM)
Flash ROM is developed on the basis of EPROM and EEPROM, its read and write speed is fast, access time can reach 20nS, so it is also called flash memory, short for flash memory.
Currently, many microcontrollers use Flash as program memory. Many Flash memories have an integrated DC/DC converter inside, which makes it possible to read, write, erase, and program using a single voltage, thus making it possible to program in the system that can be repeatedly erased more than 100,000 times and keep data reliably for more than 10 years.
Flash memory must be erased by block, each block size is variable and different manufacturers have different specifications, while EEPROM can only erase 1 byte at a time. EEPROM can only erase 1 byte at a time. It cannot replace RAM because RAM needs to be rewritten byte by by byte.
