Do you work with rigid-flex circuits, or are you planning to start? Are you constantly wondering, “what are rigid-flex circuits”? Do you know how to manufacture a rigid-flex circuit, the process for etching tracks in the board, or why a design needs modification when going from tape-out to manufacturing? If not, you’re in the right place.
Learn more about the benefits of Rigid-Flex Circuit Boards in this article. This technical article will discuss the fabrication applications and benefits of Rigid-Flex circuit boards. It will also touch on technical options for Rigid-Flex circuit boards. Before selecting a circuit board for your project, it is important to understand the benefits of Rigid-Flex circuit boards. Ultimately, you’ll have a much easier time designing and manufacturing a circuit if you choose Rigid-Flex circuit boards.
What is Rigid-Flex PCB?
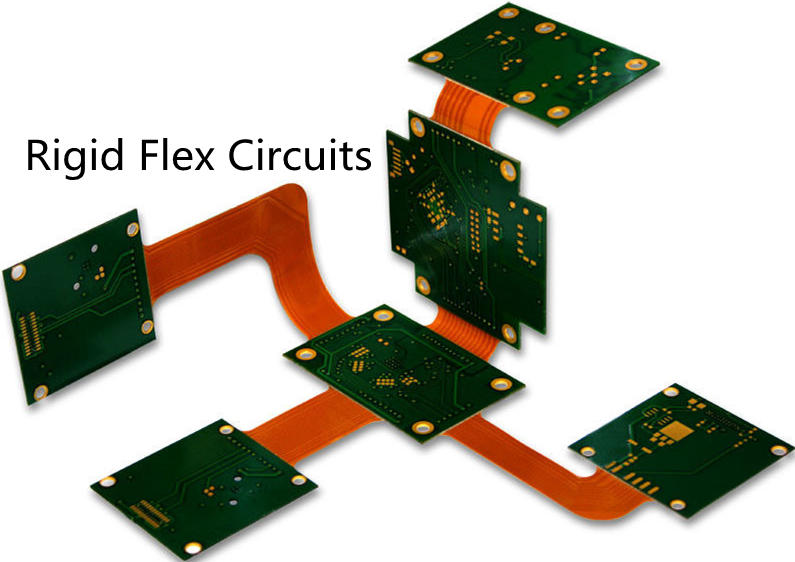
A rigid-flex printed circuit board combines the flexibility of a flexible board with the mechanical stability of a rigid board. These boards are ideal for applications that require small footprints, high mechanical stability, or a high degree of thermal stability. Additionally, rigid-flex circuit boards require fewer connectors and cables, resulting in a smaller footprint and lower cost for the system. And because they are flexible, they can be folded and installed three-dimensionally, reducing the circuit board size.
Rigid-flex PCBs require different designs and manufacturing processes. First, you must design them for the final product size, including various bending patterns and angles. For example, you can make rigid-flex PCBs bend to a certain degree, and there is a need to design this bend area carefully to avoid mechanical stress. Also, route traces are perpendicular to bend lines. In addition, you can add dummy traces to reinforce the bend area. To design rigid-flex PCBs efficiently, use a program like OrCAD PCB Designer. This software is highly optimized for rigid-flex PCBs.
Rigid-flex PCBs are commonly useful in high-precision electronic circuitry. You can make this type of PCBs from two rigid boards joined with a flex cable. The advantage of this type of board is that it allows you to increase component density without sacrificing mechanical rigidity. In addition to that, rigid-flex PCBs can fit in hard-to-reach places. As a result, you can use rigid-flex PCBs in military and medical devices, as well as in smart devices, while still maximizing reliability.
Rigid-Flex PCBs Fabrication Applications
One of the fabrication applications for rigid-flex circuits is manufacturing single-sided prototype boards. This process involves resting a dry photo-resist film on the board and exposing it to ultraviolet light. The film transfers the circuit pattern to the copper laminate, and is you expunge it chemically. The copper laminate then contains the circuit patterns and is ready for full-scale production.
The fabrication of rigid-flex PCBs requires careful consideration of thermal and mechanical issues. The presence of thermal paths or variations in copper thickness can lead to unpredictable temperatures. Therefore, it is important to thoroughly test the PCB before its assembly to avoid unnecessary expenses and wastage. Fabrication applications for rigid-flex circuits include a wide variety of applications. The manufacturing of rigid-flex PCBs can be a complex and lengthy process. However, the benefits of rigid-flex PCBs are worth every minute.
Rigorous-flex PCBs are in wide use in medical devices and the medical industry. These circuits can provide high reliability and minimize connection issues. In addition to medical equipment, we can use them in wireless communication systems and in the medical field for pacemakers. They are also cost-effective as they require less materials in their assembly process. The flexibility and reliability of rigid-flex PCBs make them ideal for high-reliability and a wide range of industries.
Other areas of application include:
- Military
- Aerospace
- Digital Cameras
- Cell Phones
- Pacemakers
- Barcode scanners and more
Benefits of Rigid-Flex Circuit Boards

There are many advantages of rigid-flex printed circuit boards. These circuits are ideal for high-density applications because they use space well. They also have the ability to withstand shock and vibration. That makes them a great choice for applications that require high accuracy and durability.
Rigid-flex PCBs are resistant to vibration and shock. This material combines the best of both flex and rigid boards. It is especially resistant to heat and extreme shocks. Rigid-flex PCBs are also more durable than conventional printed circuit boards. Rigid-flex PCBs are ideal for military applications because they can withstand extreme temperatures. Flex PCBs are also better able to withstand excessive vibration and shocks.
Rigid-flex circuit boards are more cost-effective than traditional PCBs. A rigid-flex PCB features multiple layers of flexible circuit substrates, each joined to a rigid layer. Since these circuits can bend, they’re less likely to break or malfunction prematurely. These benefits make rigid-flex printed circuit boards a great choice for smaller applications. They’re also more visually pleasing and require less assembly.
Another advantage of rigid-flex PCBs is their increased spatial efficiency. Although they take more time to manufacture, they provide more flexibility and durability. They are also easier to handle during the assembly process. And since they have fewer solder joints, assembly is easier. Further, you can fully test rigid-flex PCBs prior to installation. Ultimately, they save money and improve reliability. As a result, they’re an excellent choice for manufacturers of medical devices, smart devices, wireless controllers, and aerospace products.
Technical options for Rigid-Flex circuit boards
A variety of advanced designs are possible with rigid-flex circuit boards. They are flexible compared to conventional circuit boards, allowing for higher density and better connectivity. As a result, we often use them in high-density SMT device packaging. These circuit boards are also lightweight and can be bent into smaller sizes. Read on to learn more about some of the advantages of rigid-flex boards.
The advantages of rigid-flex circuits are many. Most of their advantages come from their flexibility and unique integration abilities. They are easy to test and you can use in harsh environments. In addition, they are flexible and well-suited for prototyping. Finally, rigid-flex circuits are typically less expensive to produce.
One of the advantages of rigid-flex circuit boards is that they are more durable than conventional PCBs. We can make a rigid-flex circuit board from polyimide, a material with high thermal stability. This material is also highly resistant to ultraviolet light and harmful chemicals. In addition, it can withstand high shocks and vibrations. This is important in sensitive electronic products, like medical devices. These boards also require less soldering.
A flex PCB’s thickness is similar to that of a rigid PCB. We can base some thickness options on the number of layers. Increasing thickness increases the overall cost. Some flex PCB thickness tables provide a guideline to determine the correct thickness. Other options include solder mask/coverlay or silk screening. Optionally, gold plating is available on the edge terminals.
Steps Involved in Rigid-Flex PCB Manufacturing Process
Because rigid-flex PCBs are so flexible, a slight flaw in the manufacturing or design can significantly affect the final product’s functionality. Hence, rigid-flex PCB manufacturers must be meticulous throughout the manufacturing process to ensure quality and reliability. With careful manufacturing, rigid-flex PCBs will be durable, lightweight, and compact.
The rigid-flex PCB manufacturing process includes several stages. The prototyping stage involves a combination of different PCB designs to create a working prototype. Since a rigid-flex PCB is unique to the intended system, it is better to make several prototypes before making the final product. It is best to consult a professional in this area and make changes before the production stage. Once you complete the prototype, send it for mass production.
Here is the step-by-step process:
- Base Material Preparation – During the rigid-flex PCB manufacturing process, copper laminate is etched. Remove anti-tarnish from the copper coil by immersing or dipping it in acid solution. Micro-etch the copper layer by using sodium persulphate to treat it.
- Generation of Circuit Patterns / Structure – You do pattern exposure or generation through screen printing or photo imaging.
- Circuit Pattern Etching – Spray a solution to your circuit pattern or dip your laminate in an etching solution. Both sides of the circuit pattern should be etched simultaneously to achieve desired results.
- Drilling Holes – Use lasers to drill holes. Laser drilling assures high precision and minimal waste.
- Through-hole Plating – Deposit copper into the drilled holes and use a chemical to plate them. It is an important step to create layers of electrical interconnections.
- Coating Etch-Resist and stripping – In this step, you apply a coat of photo-sensitive etch-resist to the substrate. Next, strip the chemical resist.
- Apply Covercoat or Cover lay – To protect the flex PCB, you should apply a cover lay over the top and bottom layers of the rigid-flex PCB. Do so by screen printing to the board’s surface before UV exposure.
- Cut the Flex – Cautiously cut individual flex boards from the production panel and attain high precision. You may use the hydraulic punching method if producing high volumes. For small volumes, you can use a special blanking knife.
- Lamination – Laminate the flex circuits between rigid sections.
- Electrical Testing & Verification – Do this as the final step in the manufacture of rigid-flex circuit boards to ensure everything is good, including circuit performance, isolation, continuity and quality.
Conclusion
The flexibility of the rigid-flex PCB allows for a wide range of uses. For example, you can use these boards for prototyping and other applications that require durability and flexibility. In addition, rigid-flex technology lasts longer than conventional tech, making it an ideal choice for electronic components subject to shocks, vibration
